Blog

Have you noticed that the month of March brings a noticeable and welcomed shift? Daylight sticks around a bit longer, schedules fill with activities, and students arrive at school each morning with a renewed sense of energy. For young multilingual learners, springtime provides a powerful opportunity; not to reinvent instruction, but to lean into what already works and let that momentum carry learning forward. By this point in the school year, students have built familiarity with classroom routines and expectations. This consistency is especially important for language learners because predictable structures—songs, chants, stories, movement, and daily oral practice—create a safe environment where students feel confident participating, even when the language feels challenging. In March, that confidence often begins to show more clearly! In March, teachers are noticing students: joining in more quickly using phrases spontaneously engaging more willingly in partner activities These moments can be easy to overlook, but they are significant indicators of language growth. Oral language development doesn’t always arrive in neat, measurable steps…it emerges through repeated exposure, joyful practice, and meaningful interaction over time. As spring energy rises (spring fever, anyone?), maintaining consistent routines can actually help classrooms feel calmer and more productive. Students know what comes next, how to participate, and what success sounds like. Rather than pulling back on structured language practice, this is the moment to protect it. Daily routines…spoken language, movement, music, and shared stories…anchor learners while giving them space to take risks. March is also a reminder that language learning is cumulative. The repetition that felt slow in the fall often pays off in the spring, when students are ready to use what they’ve internalized. When instruction continues to spiral skills like phonemic awareness, vocabulary, comprehension, and oral fluency, students are supported without feeling pressured. As the school year speeds up, this is the perfect time to take a deep breath and to notice progress. So, take time to celebrate participation, effort, and small breakthroughs to help your multilingual learner students see themselves as the capable language learner they are, and encourage them to keep moving forward! Are you ready to learn more about how GrapeSEED can help your multilingual learners succeed in ways big and small?

February is a unique moment in the school year: routines have been established, students are settled, and teachers can clearly see areas of growth as well as emerging needs. It’s also a natural pause before the busy spring months. All of this makes February an ideal time to reflect and to look ahead. For multilingual learners, what happens after the school year ends matters more than we often realize. The Summer Learning Opportunity Extended breaks can unintentionally slow language development, particularly in listening, vocabulary, and verbal confidence. However, when summer instruction is intentional and well designed, it can do more than maintain progress—it can accelerate it. The key is ensuring summer learning feels inviting, engaging, and developmentally appropriate. What Works for Young Language Learners Effective summer language programs share common elements that support growth without feeling like “more school”: A low-stress environment where students feel comfortable taking risks with language Consistent exposure to English through stories, songs, shared reading, and movement Natural repetition and routine that strengthen foundational English language skills Multi-sensory learning experiences that keep students engaged and motivated When language is experienced rather than practiced in isolation, children remain curious, confident, and connected. Why February Is the Time to Think Ahead February isn’t about making immediate decisions—it’s about asking the right questions: How can summer learning support language development without burnout? What experiences will help students feel successful and excited to learn? How can summer instruction align with the strengths of our school-year approach? Exploring these questions now allows schools to plan thoughtfully rather than reactively. A Season for Planting Ideas Strong summer programs build on what young learners love most—music, stories, movement, and interaction—while quietly reinforcing the language skills they need to grow. February offers the space to imagine a summer experience that supports continuity, confidence, and joyful learning long after winter fades. Ready to learn how GrapeSEED can be a meaningful part of your school’s summer learning?

If you’re an elementary teacher working with multilingual learners, you already know your work is full of heart, hustle, and highlighters. But let’s be honest—supporting language learners takes a lot of energy. That’s why self-care isn’t a luxury. It’s a must. You’re juggling language development, academic growth, cultural connection, and emotional support. And while your students are growing every day, you need time to recharge, too. Here’s a quick self-care recipe to keep your cup full: 🧡 Smiles: Find Joy in the Little Things Celebrate the small wins: a new vocabulary word, a student’s laugh, a kind moment. Write one highlight on a sticky note each day. It’s a mood booster—and a reminder that you’re making a difference. 🍎 Snacks: Fuel Your Body (and Soul) Don’t skip lunch! Keep a stash of healthy snacks (and maybe a treat or two) nearby. Food is fuel, and sometimes chocolate is emotional first aid. 🧠 Sanity: Protect Your Peace Say no to that extra committee if you’re overwhelmed. Take 5 minutes to breathe or stretch between lessons. Step outside during a break of any kind, even for just a second or two. Talk to someone who “gets it”—sharing helps lighten the load. You Matter Your students need you AND they also need you to be okay. When you take care of yourself, you’re showing them how to care for themselves, too. So go ahead, teacher: smile, snack, and protect your sanity. You can’t do it all , but you CAN do a lot more when you’re well. At GrapeSEED English for Children, we value teachers and work to make certain that those using our curriculum feel supported. With a personal Professional Learning Specialist that teaches can communicate with anytime, a teacher portal, on-demand PDs and so much more, we’ve got our teachers covered! Ready to learn more about getting started with GrapeSEED in YOUR classroom? Just click here for more information.

January is the season of decluttering, but in schools, it’s about clearing space for what truly matters! This month’s blog explores how thoughtful organization supports multilingual learners and why strong language systems are worth keeping. A little clarity now can create momentum that lasts all year… and beyond!

The new year is a perfect time for reflection and renewal—not just for us, but for our students, too. After a long winter break, January offers a natural opportunity to revisit and reinforce classroom routines and procedures, especially in multilingual classrooms where clarity and consistency are key to helping all students feel secure and successful. For multilingual learners, routines are more than just classroom management—they provide language-rich structures that support understanding, reduce anxiety, and foster confidence. Whether students are newcomers or have been learning English for years, a clear and predictable environment helps them focus on learning rather than guessing what’s expected. Start the month by gently reviewing procedures: entering the classroom, transitioning between activities, participating in group work, asking for help, and using classroom materials. Model each step and invite students to demonstrate, using visuals, gestures, and multilingual supports when possible. Pair verbal directions with pictures or sentence stems to help students connect words with actions. This not only aids comprehension, it builds community and shared responsibility. Remember, reviewing routines isn’t about enforcing rules—it’s about resetting the tone for a peaceful, productive, and joyful classroom. Make space for students to share what helps them learn best and celebrate the positive habits they already bring with them. By investing time in January to revisit expectations with warmth and intention, you're setting the stage for a second half of the school year filled with growth, laughter, and learning—for every student, in every language.

In today’s classrooms, elementary school teachers juggle countless responsibilities—planning engaging lessons, managing behavior, communicating with families, and differentiating instruction for every learner. Fortunately, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is opening up a world of support tools that can help educators reclaim valuable time while still meeting the diverse needs of their students. Lesson Planning, Simplified AI tools and other educator-focused platforms can generate customized, standards-aligned lesson plans in minutes. Whether you're teaching reading comprehension, performing science experiments, or developing math centers, AI can help you brainstorm activities, create differentiated tasks, and suggest formative assessments—all tailored to your students’ grade level and learning goals. Behavior Intervention Plans Made Easier Creating thoughtful, individualized behavior intervention plans (BIPs) often requires collaboration and time that’s hard to find. With the right prompts, AI can assist by generating plan templates, suggesting positive reinforcement strategies, and even helping you write goal-specific language that’s clear and professional. This allows for quicker implementation and better support for student growth. Boosting Communication with Families Need to send home a weekly newsletter, a classroom update, or a quick note in family-friendly language? AI can help you write clear, respectful, and engaging messages in seconds—and even translate them into multiple languages. This promotes stronger school-home connections without adding to your workload. More Than Just Words AI isn’t just about writing. It can generate visual aids, adapt texts for different reading levels, offer creative ideas for classroom themes, or even draft rubrics and anchor charts. When used responsibly, AI becomes a teaching assistant in your pocket—offering fresh ideas and saving you time. A Word of Caution—and Empowerment AI isn’t a magic wand, and it doesn’t replace the care, creativity, and wisdom that teachers bring to the classroom. But when used thoughtfully, it can remove some of the mental load and help you focus on what matters most: building relationships, inspiring learners, and making a lasting impact. AI can be a game-changing tool for educators—not by replacing the human touch, but by enhancing it. With the right approach, you can use AI to create, communicate, and collaborate more efficiently—without sacrificing quality. Just as AI can support teachers in the classroom, GrapeSEED does the same. From intentionally designed lesson plans to materials at your fingertips, to a results driven, joy filled curriculum for your language learner students, GrapeSEED has it all. Click here to learn more !

If you’ve ever looked at your lesson plans and thought, “There’s no way I can fit all this in,” you’re not alone. Teachers today face an ever-growing list of standards, assessments, and initiatives, all while striving to create joyful, meaningful learning experiences for young children. The struggle is real! So how can we honor curriculum expectations without overwhelming ourselves or our students? Read on for ideas and strategies! Start with What Matters Most Not everything carries equal weight. Identify the skills and concepts your students truly need to succeed, both academically and developmentally. Prioritize depth over breadth when possible. A well-understood concept is more valuable than one that’s been rushed and checked off a list. Integrate Across Subject Areas Look for ways to blend content. A science lesson can include reading comprehension. A writing activity can connect to social studies. Integration allows for richer, more efficient learning and saves time while deepening student understanding. Protect Time for Play, Talk, and Joy Children learn best when they are engaged and emotionally connected to content. Carve out time for class discussions, movement, and creative exploration. These “non-academic” moments often bring about the deepest learning and are critical for social-emotional development. Be Realistic, Not Perfect It’s okay if not every lesson goes as planned or every objective is met on the first try. Focus on consistent growth, not perfection. Trust your professional judgment. After all, you know your students best. Support One Another Collaboration is key. Talk with teammates about what’s working, what can be scaled back, and how to share the load. A balanced curriculum starts with a balanced teacher, and that balance often comes from working together. Remember, you aren’t just covering content, you’re helping to shape children’s lives. When we prioritize purposeful, joyful learning over packing it all in, we give students (and ourselves) what truly matters most.. To learn how GrapeSEED English for Children saves teachers time so that they can focus on what is important, click here today!

What is inevitable in most schools across the United States? Standardized testing! And for our English Language Learner students, there is no getting around it... standardized tests are nonnegotiable. So, what is the challenge for elementary teachers and administrators? Striking the right balance. The key to that balance is preparing children for these assessments without completely tossing out developmentally appropriate instruction AND without creating anxiety. Why Preparation Matters While standardized tests might not capture the full range of our students' growth, they do influence school accountability, placement decisions, and even the allocation of funding and other resources. So, we prepare our students…not by ‘teaching to the test’, but by giving them the skills that they need to feel comfortable and confident during testing time. Multilingual learners, especially, benefit when we scaffold their testing experience, making sure they understand test formats, directions, and strategies, so they can truly show what they know. Ready for a few practical test prep ideas? Let’s dig in! Meaningful and Age-Appropriate Strategies 1. Build Familiarity Through Routine Incorporate test-like questions into regular classroom activities in a low-stakes way. Use short passages, multiple-choice questions, and timed activities that mimic test conditions, without the pressure. 2. Focus on Language and Concept Development ELL students need time to develop academic vocabulary and comprehension skills. Embed test-related language (e.g., “main idea,” “infer,” “evidence”) into their daily instruction in ways that make sense contextually. 3. Use Play and Movement For younger learners, active learning helps reinforce skills. Try review games, partner quizzes, or station rotations. These help students internalize content and practice test-taking skills in an engaging, age-appropriate format. 4. Practice Metacognition and Self-Talk Teach simple test-taking strategies like rereading the question, eliminating wrong answers, and checking work. Model “think alouds” to show how good test-takers reason through tricky questions. 5. Support Emotional Readiness Let students know that tests are just one way to show learning. Create a calm, encouraging classroom culture that frames testing as a chance to “show what you’ve learned,” not a judgment on their worth or ability. A Final Thought for Administration Administrators play a vital role in ensuring that multilingual learner teachers are supported with training, resources, and realistic expectations. Providing carved out time for your teachers to focus on standardized test readiness and making room for differentiated assessments, shows your support and commitment. When done thoughtfully, preparing your students for testing time can reinforce key skills, boost their confidence, and ensure that every student…especially our multilingual learners…have a fair chance to succeed. Are YOU looking for the best way to support your multilingual learner students? Then YOU’RE looking for GrapeSEED! Click here to learn more.

Are you a teacher of multilingual learners? If you’re answer is a resounding ‘YES’, then you have very likely heard the term ‘comprehensible input’ over and over again. But what does it actually mean and why does it matter so much? Comprehensible input is simply language that is just a teeny bit above a student’s level of understanding, but that can make sense and be understood with the scaffolds of context (like a story, for example), realia, props, gestures, facial expressions and so on. When your students receive this type of input during lessons, they are going to acquire language more naturally and effectively. You might be wondering, ‘why is this so important in my ESL classrooms?’ The answer is because language acquisition thrives on understanding. When students have a high level of anxiety because they’re overwhelmed with unfamiliar vocabulary and speech that is super-fast, they’re very likely to just ‘shut down.’ However, when we as teachers mindfully make our input very clear and add those scaffolds mentioned, children grow in confidence and are much more willing to engage and take academic risks. Try these easy yet effective strategies to build comprehensible input into your lessons: o Use props and realia: Using real life objects, props and pictures makes a big impact! Showing a picture of a tree while saying “This is a tree” makes meaning click instantly. o Slow your pace and use gestures: Use a moderate pace when speaking and be certain to pronounce words clearly. Use body language to support what you’re saying, when appropriate. Remember that a smile and a well-planned gesture can go a long way when building comprehensible input. o Repeat and rephrase: Saying things in a different way when is seems as though your point didn’t get across can be key. For example, if “Let’s line up” causes confusion or misunderstanding, try “Get in a line, please…one behind the other.” o Build on the ‘known’: Connect new learning to things that your students have already learned or experiences. This makes new information feel much more familiar and easier to grasp. o Check for understanding: Use short sentence frames and yes/no & either/or questions to check for understanding in a way that is low stress for your students. Remember, comprehensible input isn’t about “dumbing down” language—it’s about making it meaningful and accessible. When students understand what they’re hearing or reading, they’re more likely to respond, participate, and grow. And that’s when the real language magic begins! Does the GrapeSEED English for Children curriculum include comprehensible input? Yes, it definitely does, and in multiple ways! Learn all about it, along with how YOU can get started with GrapeSEED, by clicking here .

Welcoming your youngest newcomer children to school … children who are new to the United States and adjusting to a new language, a new culture, and new way of ‘doing school’… requires so much more than just academic support. One of the most significant but most often overlooked challenges that brand-new newcomer children face is learning to self-regulate in this very new, very different looking learning environment. As teachers and administrators, supporting the cultivation of self-regulation skills in newcomer students not only supports their academic success, but their emotional well-being and sense of belonging, too. Understanding the Challenge Many newcomer students arrive with limited or interrupted schooling and likely have experienced some sort of trauma, migration stress, and culture shock. These factors can make self-regulation … managing emotions, behavior, and attention … especially difficult. Unfamiliar expectations around classroom behavior, routines, and interactions with classmates can contribute to feelings of confusion or frustration. So what can you do? Practical Strategies for Educators: 1. Build Predictable Routines: Clear, consistent daily routines help reduce anxiety and give students a sense of safety. Pictorial schedules and transition cues can be especially helpful for English language learner students. 2. Teach Vocabulary dealing with Emotions : Young newcomers may struggle to express emotions in a new language. Using facial expression cards and simple language to build a shared emotional vocabulary that supports communicating feelings will make a huge impact on building the sense of community needed in your school and classrooms. 3. Model and Practice Self-Regulation: Use modeling and role-playing to demonstrate strategies like taking deep, slow breaths, counting, or just taking a break can make a powerful impact. Also, consider creating a calm-down corner in your school or classroom where students can go to ‘reset’. 4. Establish Culturally Responsive Relationships: Learn about students’ cultural backgrounds and show curiosity and respect. Trusting relationships provide the foundation for students to feel safe enough to practice self-regulation. 5. Partner with Families and Specialists : Collaborate with other multilingual learner teachers, counselors, and families to ensure a unified approach. Remember that while they could be struggling to acclimate a bit themselves, parents and families can offer insight into what comforts and motivates their children. Supporting self-regulation is a journey, not a quick fix. With empathy, structure, and cultural sensitivity, we all can help newcomer students develop the emotional tools they need to flourish, both in and out of the classroom. At GrapeSEED, our curriculum is built on a foundation that encourages a calm, joy filled environment. Our daily lesson plans incorporates a low affective filter for students at every turn as they acquire English. Ready to learn more? Click here!

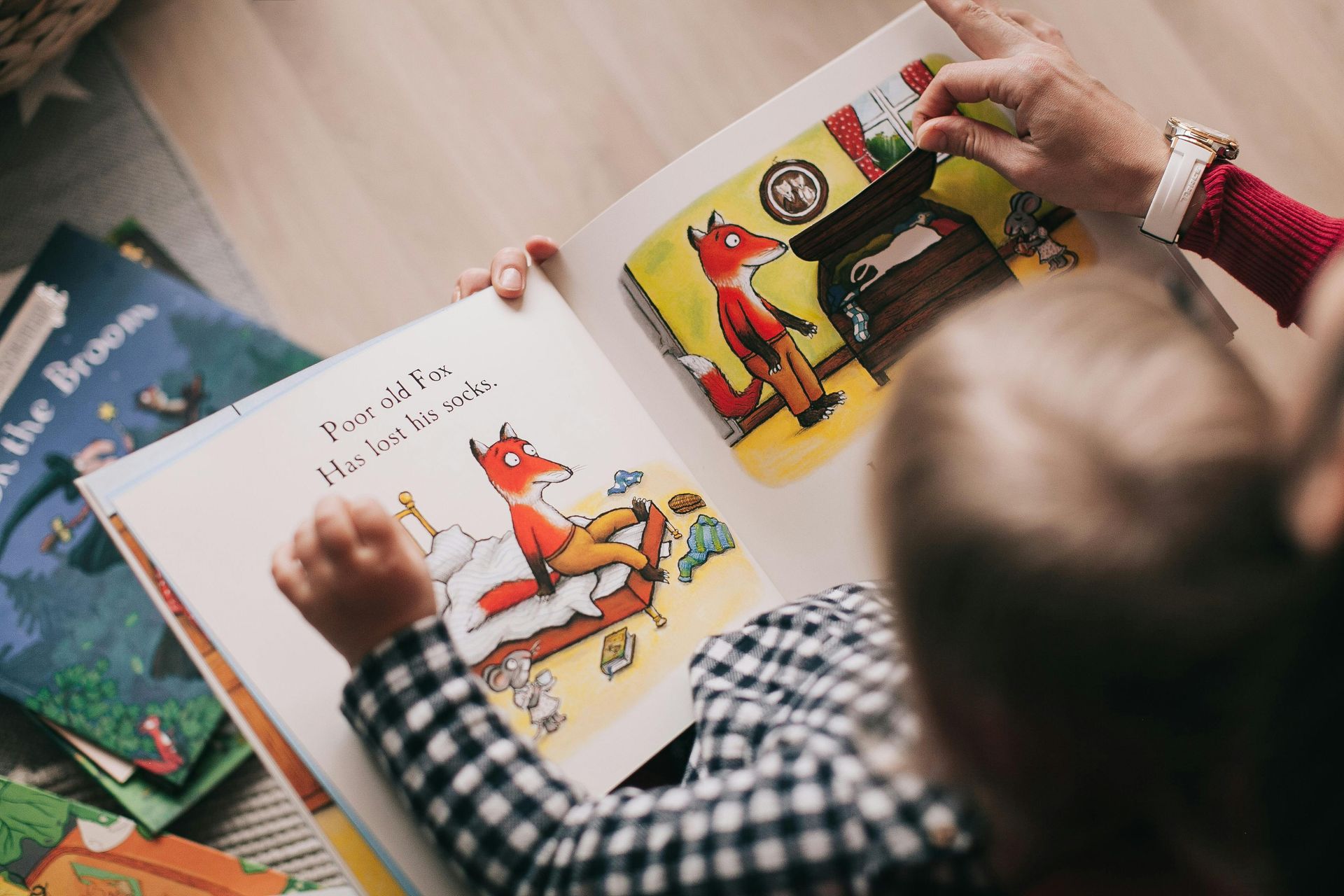
There’s something magical about the first few weeks of school; the fresh notebooks, sharpened pencils, and bright-eyed students walking through your classroom door, each with a story ready to unfold. As teachers, we don’t just teach content; we build communities. And when our classroom becomes a place where every student feels seen, heard, and valued, that’s when real learning begins.

As the new school year begins, one of the most powerful things a teacher can do is create a strong, inclusive classroom community—especially for multilingual learners! Such students bring rich linguistic and cultural assets, but they also face the challenge of navigating a new environment, language, and often, academic expectations. Building a sense of belonging early on helps students feel safe, seen, and motivated to participate and succeed. Start with Relationships Before jumping into academics, focus on getting to know your students and letting them get to know you. Learn their names correctly and use them often. Invite students to share about their cultures, home languages, interests, and goals. Use visuals, gestures, and sentence starters to support their sharing. When you show genuine interest in who they are, students begin to feel that they belong. Create a Welcoming Environment Make sure your classroom reflects the diversity of your students. Include books, posters, and materials in multiple languages. Greet students in their home languages and celebrate multilingualism as a strength. Posting a simple welcome message in every student’s heritage language can make a big difference on the first day. Use Language to Build Community Even when students are still developing English skills, they can participate meaningfully in community-building activities. Use pair and group work, cooperative games, and art-based projects that allow for communication beyond just spoken or written words. Encourage all forms of expression and use language scaffolds like word banks, sentence frames, and visuals. Partner with Families Strong relationships with families reinforce the classroom community. Send home multilingual newsletters or videos. Invite families to share traditions, stories, or even music. When families feel welcomed, students feel even more connected. The beginning of the school year sets the tone for everything that follows. When multilingual learners feel like valued members of the classroom from day one, they’re more likely to engage, take risks, and thrive. Building community isn’t just a warm-up—it’s the foundation of effective teaching! Ready to learn about how GrapeSEED’s English Language Acquisition Curriculum can propel your multilingual students to success? Just click here .
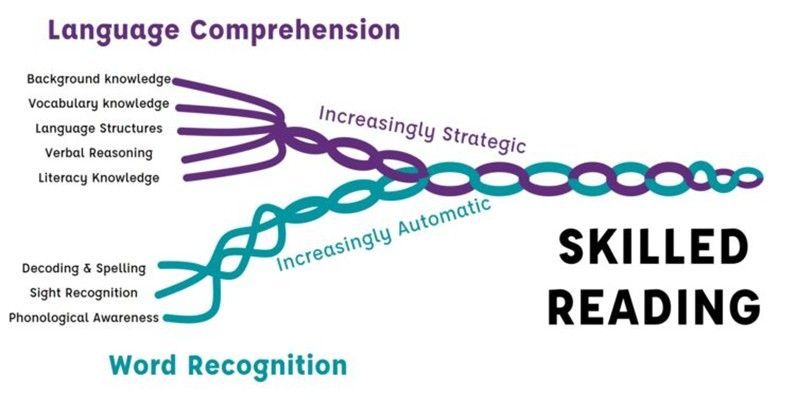
In the realm of literacy education, few models have provided as much clarity and insight as Scarborough’s Reading Rope . Created by Dr. Hollis Scarborough in 2001, this visual metaphor elegantly breaks down the complex, intertwined skills involved in becoming a proficient reader. Whether you’re a teacher, literacy coach, or parent looking to support young readers, understanding this model is key to fostering effective instruction and targeted intervention. In this blog, we’ll explore what Scarborough’s Reading Rope is , how it works, and how educators can use it as a framework for teaching reading . By the end, you’ll have Scarborough’s Reading Rope explained in detail—bringing you closer to mastering the art and science of reading instruction. Table of Contents Introduction to Scarborough’s Rope Model of Reading The Origin of Scarborough’s Reading Rope Breaking Down the Strands: Language Comprehension Breaking Down the Strands: Word Recognition How the Strands Work Together Why Use the Reading Rope for Teaching Reading? Scarborough’s Rope Model vs. Other Reading Theories Practical Applications in the Classroom Scarborough’s Reading Rope Explained for Parents

Greetings, esteemed educators and fabulous school staff! The final bell is ready to ring, the chalk has settled, and the classroom doors will soon be closed. It’s just about time to hang up those lanyards and tuck away the lesson plans, because summer vacation is nearly here. Cue the confetti and bring in the beach balls—let’s talk about making the most of your well-deserved break!

Reading is more than just recognizing words on a page—it’s about understanding, interpreting, and interacting with the text. That’s where reading comprehension comes in. Whether you're a parent looking to support your child's literacy skills, a teacher aiming to refine your approach, or an adult seeking to improve your own understanding, boosting reading comprehension is a critical goal. Fortunately, there are proven strategies and engaging activities that can make a significant difference. Reading comprehension refers to the ability to process text, understand its meaning, and integrate it with existing knowledge. It’s a multi-layered cognitive process that involves far more than simply recognizing words on a page. At its core, comprehension is about making sense of what is read, constructing meaning from both the text itself and the reader’s own experiences and background knowledge. Effective reading comprehension requires the simultaneous coordination of several complex skills: Decoding – Accurately translating written words into spoken language, which is foundational to all reading. Vocabulary Knowledge – Understanding the meaning of words and phrases, especially in context. The richer a reader’s vocabulary, the better equipped they are to grasp more nuanced or technical texts. Syntax and Grammar Understanding – Comprehending sentence structures and punctuation, which guide the reader in interpreting meaning and tone. Making Inferences – Reading between the lines to understand what is implied but not directly stated. Inference-making requires combining textual clues with prior knowledge. Critical Thinking – Evaluating arguments, comparing ideas, identifying bias, and distinguishing fact from opinion are all higher-level processes involved in deep comprehension. Monitoring Understanding (Metacognition) – Skilled readers are aware of when they don’t understand something, and they know strategies—like rereading, questioning, or summarizing—to fix breakdowns in comprehension. Reading comprehension can be thought of as a dialogue between the reader and the text . Rather than passively absorbing information, the reader actively constructs meaning by asking questions, making predictions, and drawing conclusions. Strong comprehension also allows readers to retain what they’ve read and apply it in new situations, whether for academic learning, professional tasks, or daily decision-making. Ultimately, reading comprehension is not a static skill—it grows over time with practice, exposure to diverse texts, and the application of intentional reading strategies. In this blog, we’ll explore how to improve reading comprehension through practical strategies, targeted exercises, differentiated methods for age groups, and literacy connections across subjects. You’ll also find motivational tips and a robust toolkit of activities to help any learner become a more confident and insightful reader. What is Reading Comprehension? Reading comprehension refers to the ability to process text, understand its meaning, and integrate it with existing knowledge. It’s a multi-layered cognitive process that includes decoding, vocabulary understanding, inference-making, critical thinking, and metacognition. Effective comprehension allows readers to: Grasp the main idea of a text Understand and infer meaning from context Analyze, interpret, and evaluate content Retain and apply information Make connections to personal experience or other texts Reading comprehension can be divided into two categories: literal comprehension (what is explicitly stated) and inferential comprehension (what is implied or derived through reasoning). Mastering both is essential for academic success and lifelong learning. Why Is Reading Comprehension Important? The impact of strong comprehension skills stretches far beyond the classroom: Academic Achievement : From science labs to history lessons, comprehension skills determine how well students can learn across all subjects. In standardized tests, it's often reading comprehension—not background knowledge alone—that determines success. Problem-Solving Skills : Comprehension nurtures the ability to compare, contrast, deduce, and reason. These are foundational skills for decision-making and analytical thinking in everyday life. Professional Success : Jobs in nearly every field require the ability to comprehend reports, emails, instructions, and contracts. Comprehension is a lifelong asset in the workplace. Empathy and Perspective-Taking : Reading narratives builds emotional intelligence by allowing readers to see the world through different characters' eyes. Informed Citizenship : Understanding news, laws, and social issues requires comprehension of complex texts. A literate society is a more informed, engaged one. Common Challenges in Reading Comprehension Every reader, regardless of age or experience, can encounter roadblocks. Understanding these challenges allows educators and parents to target solutions more effectively: Vocabulary Gaps : Without a strong grasp of the words used, readers may miss the meaning of entire passages. Beyond reading, a limited vocabulary also affects oral communication and writing skills . Students with fewer words at their disposal may struggle to express themselves clearly, both in conversations and in written assignments. This can lead to frustration, social withdrawal, and reduced classroom participation. They might be hesitant to speak up during group discussions or may offer overly simplistic responses, which can affect teachers’ perceptions of their abilities. In time, this hesitancy can undermine a child’s confidence and willingness to engage academically. Perhaps most concerning is the long-term academic trajectory associated with vocabulary deficits. Research has consistently shown that early vocabulary knowledge is one of the strongest predictors of later reading success and overall academic achievement. Without strong word knowledge, students are at risk of falling behind—not only in reading but across all content areas where comprehension is critical, such as science, history, and math. As they progress through school, texts become more complex, and students are expected to understand abstract concepts and subject-specific terms. Without a well-developed vocabulary, they face an uphill battle in every academic area. Ultimately, closing the vocabulary gap early is essential for leveling the playing field. Exposure to rich language experiences—such as read-alouds, conversations, explicit vocabulary instruction, and varied reading materials—can significantly help bridge this divide. For educators and caregivers, recognizing and addressing vocabulary gaps early on is not just about improving test scores—it's about giving every child the tools to access knowledge, express themselves confidently, and succeed in school and life. Lack of Background Knowledge : Prior knowledge acts as a scaffold for understanding new concepts. When it's absent, comprehension suffers. Passive Reading Habits : Simply moving eyes across text without interaction leads to shallow understanding. Difficulty with Text Structure : Some students don’t understand how informational texts are organized, such as headings, captions, and transitions. Limited Attention Span : Particularly in digital environments, sustaining focus on lengthy or dense texts is a growing challenge. Fortunately, these issues can be addressed with the right strategies, support, and practice. How to Improve Reading Comprehension: Core Strategies Let’s explore core strategies that form the foundation for strong comprehension. Each is backed by research and effective across multiple age groups. 1. Preview and Predict Encourage readers to look at the title, subheadings, images, and introductory paragraphs before reading. Ask them to make predictions. This activates their prior knowledge and gives them a purpose for reading. Example: “We’re about to read an article about coral reefs. What do you already know about ocean life?” 2. Set a Purpose for Reading Are you reading to answer a question? To compare characters? To understand a process? Setting a purpose guides the reader’s attention. Tip: Give students a question to answer or a goal to achieve as they read. 3. Teach Vocabulary in Context Direct vocabulary instruction, especially for tier 2 and tier 3 words (academic and subject-specific), is crucial. Strategy: Use “word webs” to explore new vocabulary, including synonyms, antonyms, and usage in sentences. 4. Use Graphic Organizers Visual aids help readers break down information and see relationships between ideas. Venn diagrams Story maps KWL charts (Know, Want to Know, Learned) Cause and effect charts 5. Teach Summarization and Paraphrasing Summarizing helps identify key points, while paraphrasing ensures readers can explain what they've read in their own words. Activity: After reading, challenge students to write a one-sentence summary or create a five-word “headline” for the passage. 6. Model Think-Alouds Teachers or parents should verbalize their thought process while reading. This metacognitive approach demonstrates how skilled readers approach a text. Think-alouds are powerful because they teach metacognition , or "thinking about thinking." Many students who struggle with comprehension don’t realize that proficient readers constantly monitor their understanding, reread confusing sections, and make mental notes or connections as they go. By listening to someone model this, students begin to adopt similar habits. For example, while reading a story, a teacher might say, “Hmm, I wonder why the character chose to do that… I’m going to keep reading to see if I find out.” This helps students see that reading is an active process, not a passive one. Several strategies can be incorporated into a think-aloud: Predicting – Ask students to anticipate what might happen next or what the text might be about based on the title or headings. For instance, “Based on this chapter title, I think the character is going to face a big challenge.” Questioning – Pose questions during reading to promote engagement and critical thinking. For example, “Why is this event important? I wonder if it connects to the main idea?” Clarifying – Model what to do when something is confusing. A reader might say, “That sentence was a little tricky. Let me read it again more slowly.” or “I’m not sure what this word means—can I use the rest of the sentence to figure it out?” Visualizing – Encourage creating mental images. For example: “I can picture this scene in my mind—it’s like watching a movie.” This helps especially with descriptive or narrative texts. Making Connections – Relate the text to personal experience, other books, or world events. Say, “This reminds me of another story we read where the character had to make a tough choice.” 7. Encourage Text Connections Help students connect what they read to: Their own lives (Text-to-Self) Other texts (Text-to-Text) The world around them (Text-to-World) Reading Comprehension Strategies by Age Group Comprehension instruction isn’t one-size-fits-all. Here’s how strategies can be tailored for different age levels. Early Elementary (Grades K–2) Focus on listening comprehension, story structure, and vocabulary development. Use picture books with clear plots Ask “Who, What, When, Where, Why” questions Use puppets and props for story retelling Repeated reading builds fluency Upper Elementary (Grades 3–5) Start introducing nonfiction text structures and inference-making. Use graphic organizers and story maps Teach how to cite evidence Practice summarizing longer texts Begin using chapter books and age-appropriate news Middle and High School Shift to critical reading, text analysis, and synthesis. Explore multiple genres and perspectives Teach annotation and close reading skills Discuss bias, argument structure, and tone Assign research-based reading projects Adult Learners Focus on practical texts (forms, manuals, job applications) and informational reading. Use real-life materials Teach skimming and scanning techniques Emphasize vocabulary building and summarizing Practice reading aloud to build fluency Literacy Across Content Areas Comprehension isn’t just for English class—it’s essential across all disciplines: Science : Understanding experimental procedures and technical vocabulary Social Studies : Analyzing historical documents, maps, and arguments Math : Interpreting word problems and understanding instructions Arts : Analyzing themes and visual narratives in poetry, music, and images Teachers should explicitly teach reading strategies that are subject-specific. For example, teach how to break down a scientific article or how to interpret a graph in social studies. The Role of Motivation in Comprehension Comprehension improves when students are motivated to read . Here's how to foster that intrinsic desire: Choice : Let students choose books based on their interests. Autonomy boosts engagement. Purpose : Connect reading to real-life applications. Why does this matter? Community : Book clubs, reading circles, and peer discussions make reading social. Success : Ensure books are at the right level—not too easy, not too hard. Readers should feel challenged, not defeated. When students read because they want to—not because they have to—deeper comprehension naturally follows. Tips for Parents and Educators Parents Model reading for enjoyment—let children see you reading. Discuss books after reading instead of just asking “Did you like it?” Use books as conversation starters around values, challenges, and relationships. Reinforce reading during daily routines (e.g., menus, signs, recipes). Educators Set aside time for independent reading in the classroom. Integrate comprehension instruction into every lesson, not just ELA. Use formative assessments like exit slips or reading logs. Collaborate with school librarians to build interest-based reading lists. Measuring Progress in Reading Comprehension Assessing comprehension can be qualitative or quantitative: Observational Tools : Watch how students annotate or respond to questions. Written Assessments : Use short-answer responses and summaries. Conversations : Ask open-ended questions to gauge depth of understanding. Digital Platforms : Many apps track data over time (e.g., fluency, question accuracy). Remember: Progress may not always be linear, but consistency in reading and reflection yields long-term gains. Final Thoughts Improving reading comprehension is not about speed or memorization—it’s about thinking . It’s about connecting with a text in a way that activates curiosity, builds empathy, and deepens understanding. Whether you're working with a struggling reader or a student who loves books, the key is to create an environment where reading is meaningful, challenging, and enjoyable. Equip learners with strategies, give them space to explore, and celebrate their growth along the way. With the tools, strategies, and activities provided here, you’re well-positioned to guide any reader—young or old—toward becoming a more confident, thoughtful, and enthusiastic reader.

In 2025, teacher appreciation has taken on an exciting new dimension. As we navigate through a rapidly evolving digital age, the role of teachers has become more crucial and multifaceted than ever before. Here’s why celebrating our educators this year is both special and unique: Digital Pioneers : Teachers today are not just educators but also pioneers of digital learning. They've seamlessly integrated technology into their classrooms, using tools like virtual reality and AI to create immersive learning experiences that captivate and engage students. Adaptability at its Best : The past few years have shown us the incredible adaptability of teachers. Whether transitioning from in-person to online classes or adopting hybrid teaching models, teachers have proven their ability to pivot and innovate, ensuring that learning continues uninterrupted. Champions of Personalized Learning : With the help of data-driven insights and educational technology, teachers are crafting personalized learning experiences. This approach caters to the unique needs of each student, fostering an environment where everyone can thrive at their own pace. Emotional Intelligence Leaders : Teachers today understand the importance of emotional intelligence in education. They are equipped to support the emotional and mental well-being of their students, creating a safe and nurturing space for learning. Creative Engagement : From gamified learning to interactive projects, teachers are continuously inventing new ways to make education fun and engaging. Their creativity inspires students to be curious and passionate about their subjects. As we look to the future, the role of teachers will continue to evolve, but one thing remains constant: their unwavering dedication to shaping young minds. In 2025, we celebrate not just their adaptability but also their commitment to fostering a brighter future for all. Teacher appreciation today is a testament to their invaluable contributions to society and the endless possibilities they unlock for future generations. At GrapeSEED, we are inspired by and appreciative of teachers who inspire, innovate, and ignite a love for learning! Are YOU ready to become a GrapeSEED teacher? Click here!

The role of an instructional coach in the multilingual language learner world is challenging and rewarding, requiring a unique set of skills and a deep commitment to fostering language acquisition among diverse learners. Often serving as the bridge between teachers and students, instructional coaches in this realm play a pivotal role in shaping how language education is delivered and experienced. Here's a closer look at the nuances of this impactful role: Supporting Diverse Learners One of the most rewarding aspects of being an ESL instructional coach is the opportunity to support a wide range of learners from various cultural and linguistic backgrounds. This diversity enriches the learning environment but also presents unique challenges. Coaches must be adept at understanding the specific needs and strengths of each student, tailoring strategies to enhance engagement and comprehension. Adapting Teaching Strategies Cultural context plays a critical role in how language is taught and learned. ESL instructional coaches must continuously adapt teaching strategies to align with the cultural nuances of their students. This involves integrating culturally relevant materials, respecting different learning styles, and being sensitive to the cultural references that may affect language comprehension and usage. Fostering Collaboration Collaboration is at the heart of an ESL instructional coach's work. Coaches collaborate with teachers to develop effective lesson plans, provide feedback on teaching practices, and introduce innovative instructional methods. By fostering a collaborative environment, coaches help create a supportive network that enhances professional growth and improves student outcomes. Continuous Professional Development To stay effective, ESL instructional coaches must engage in continuous professional development. This includes attending workshops, participating in webinars, and staying abreast of the latest research in language acquisition and teaching methodologies. Professional development is crucial for coaches to refine their skills and introduce new teaching techniques that can benefit both teachers and students. Leveraging Technology The integration of technology in ESL instruction is a game-changer, and instructional coaches are at the forefront of this transformation. By leveraging tools such as language learning apps, virtual classrooms, and digital assessments, coaches can enhance the learning experience and provide more personalized support. Technology also allows for greater accessibility, enabling students to practice language skills outside the traditional classroom setting. Making a Lasting Impact Ultimately, the role of an ESL instructional coach is about making a lasting impact on the lives of students and educators. Coaches help unlock the potential of students by equipping them with the language skills needed to succeed in a globalized world. They also empower teachers with the tools and confidence to deliver effective ESL instruction. In conclusion, being an instructional coach in the ESL world is a dynamic and fulfilling career that requires a blend of empathy, adaptability, and expertise. By embracing these nuances, instructional coaches can contribute significantly to the field of language education, paving the way for a more inclusive and effective learning environment. Are you an instructional coach who is interested in learning about the impact that GrapeSEED could make on your teachers and students? Come partner with us! Just click here to get started.

In the dynamic environment of multilingual learner classrooms, data-driven instruction paired with formative assessments plays a pivotal role in creating effective and engaging learning experiences. Let's explore how these strategies can benefit both teachers and students. The Power of Formative Assessments Formative assessments are essential tools that offer real-time insights into student progress, enabling educators to refine their teaching methods. Here's why they're indispensable: Immediate Feedback : By providing instant insights, formative assessments help teachers adjust their instructional strategies to better meet student needs. Customized Learning : These assessments allow lessons to be tailored to individual student needs, moving away from generic approaches to more personalized instruction. Increased Engagement : When lessons are precisely aligned with a student's current understanding, engagement and participation naturally increase. Effective Formative Assessment Techniques Incorporating a variety of assessment techniques keeps the classroom lively and informative: Quizzes : These quick assessments help identify which language concepts students have mastered and which need more attention. Peer Reviews : Students work together to provide feedback, fostering a collaborative and supportive learning environment. Self-Assessments : Encouraging students to evaluate their own progress promotes self-awareness and active participation in their learning journey. Benefits of Data-Driven Instruction Utilizing data from formative assessments allows for a more strategic approach to teaching: Targeted Instruction : Teachers can develop activities that address specific areas of difficulty, such as pronunciation exercises or vocabulary games. Supportive Learning Environment : Continuous feedback nurtures a growth mindset, encouraging students to view learning as an ongoing process. Enhanced Language Acquisition : Focusing on individual language skills helps students build a robust foundation for more rapid and confident language learning. In summary, integrating data-driven instruction with formative assessments transforms the ESL classroom into an engaging and effective learning space. By using these strategies, educators can better support student growth and development, ultimately leading to more successful language acquisition. If you would love to learn about the GrapeSEED Curriculum and our formative assessments, known as ‘Quick Checks’, just head to our website by clicking here .

Welcome to the world of dynamic learning, where initiation and perseverance are the secret superhero skills every elementary school student needs! These executive function skills are the power-ups that help students start tasks with enthusiasm and stick with them until the very end. Let's dive into some creative ways to nurture these skills and make your classroom a hub of engaged learners! Why Initiation and Perseverance Matter: Cultivating initiation and perseverance in students is like giving them the keys to academic success. These skills not only help students tackle homework and projects but also prepare them for real-world challenges. By fostering these abilities, you're equipping your students with resilience and self-motivation that will serve them beyond the classroom. Strategies to Encourage Initiation: Start with a Bang : Kick off lessons with intriguing questions or exciting stories to capture students' curiosity. For example, "What if you woke up one day as a superhero? What would your first mission be?" Break It Down: Teach students to divide tasks into smaller, manageable steps. This makes starting less daunting and gives them a clear path forward. Choice Boards: Offer a variety of activities related to the lesson topic and let students pick their starting point. This autonomy boosts their interest and willingness to begin. Classroom Challenges: Set up light-hearted competitions where students can earn points or badges for starting tasks promptly. Who doesn’t love a little friendly rivalry? Building Perseverance: Praise the Process: Focus on effort and strategy rather than just results. Celebrate when students try different approaches and persist through difficulties. Goal Setting: Encourage students to set personal learning goals and track their progress. Seeing small wins adds up to big motivation! Reflection Time: Allow time for students to reflect on what they’ve learned from their challenges. This helps them understand that every hurdle is a learning opportunity. Perseverance Stories: Share stories of famous figures who overcame obstacles. Discuss how perseverance played a role in their success and relate it back to students' own experiences. Fun Activities to Reinforce These Skills: Initiation Stations: Create activity stations around the classroom that students can choose to start with. Each station could have a unique, fun challenge that aligns with the lesson. Perseverance Puzzles: Use puzzles or brain teasers that require patience and strategy. Working through these together can be a rewarding class exercise. Story Time Heroes: Have students write short stories featuring characters who overcome obstacles through perseverance. This can be a creative writing exercise that doubles as a life lesson. Empowering students with the skills of initiation and perseverance transforms your classroom into a vibrant learning environment. By implementing these strategies, you'll help your students become proactive, determined, and ready to tackle any challenge with a smile. Here’s to a classroom full of unstoppable learners! If you would love to learn how GrapeSEED can positively impact your students, just click here!

Metacognition refers to the awareness and understanding of one's own thought processes. It involves self-regulation and reflection on how we learn and think, enabling learners to plan, monitor, and evaluate their understanding and performance. Working memory, on the other hand, is the ability to hold and manipulate information in the mind over short periods. It is crucial for reasoning, learning, and comprehension. Importance in Learning Both metacognition and working memory are vital for academic success. Metacognition empowers students to become independent learners by actively managing their cognitive processes. It helps in setting goals, selecting strategies, and assessing the effectiveness of these strategies. Working memory is essential for tasks such as problem-solving and following instructions, directly impacting a student's ability to engage with and process new information. Strategies to Build Metacognition and Working Memory Self-Reflection Exercises: Encourage students to engage in self-reflection by asking them to think about what strategies they used in learning a topic and which were most effective. Journaling about their learning process can help them become more aware of their cognitive strategies. Mnemonic Devices: Use mnemonic devices to enhance working memory. Techniques such as acronyms, visualization, and rhymes can help students remember complex information by associating it with familiar concepts. Chunking Techniques: Teach students to break down large amounts of information into smaller, manageable chunks. This strategy can help enhance working memory by reducing the cognitive load and making it easier to process and recall information. Applying Strategies in Educational Settings Incorporate Self-Assessment: Regular self-assessment helps students practice metacognitive skills. Teachers can provide tools such as checklists or self-questioning techniques to guide students in evaluating their learning. Interactive Learning: Use interactive activities like group discussions and peer teaching to encourage students to verbalize their thought processes, thereby enhancing their metacognitive awareness. Visual and Auditory Aids: Incorporate visual and auditory aids to support memory retention. Diagrams, charts, and multimedia presentations can cater to different learning styles and aid in memory consolidation. By integrating strategies that promote metacognition and working memory, educators can significantly enhance students' learning experiences. Encouraging self-reflection, utilizing mnemonic devices, and implementing chunking techniques can equip students with the tools they need to become effective and independent learners. These skills not only bolster academic achievement but also prepare students for lifelong learning and problem-solving. Intrinsic motivation? Interactive learning? Visual and auditory aids? Did someone say GrapeSEED? To learn more about how we incorporate the strategies mentioned in this article AND MORE into our curriculum and teaching strategies, just click here .

In the bustling environment of an elementary classroom, harnessing students' attention and self-control can seem daunting, yet these executive functioning skills are crucial for academic success and personal development. As educators, nurturing these skills can empower students to become more focused, resilient, and independent learners. Here’s how teachers can integrate strategies, such as structured routines, mindfulness exercises, and interactive activities, to cultivate these capabilities in young learners. Structured Routines: The Backbone of Classroom Management Establishing a consistent daily routine is a fundamental step in helping students master self-control and attention. Predictable schedules provide a sense of security, helping students understand what is expected at different times of the day. Teachers can start by outlining the day’s agenda at the beginning of each class, using visual aids like charts or calendars. This not only sets clear expectations but also helps students mentally prepare for transitions between activities. Gradually, students learn to manage their time and maintain focus, knowing exactly what comes next. Mindfulness Exercises: Building Inner Focus Incorporating mindfulness exercises into the classroom can significantly enhance students' ability to concentrate and regulate their emotions. Simple activities, such as guided breathing or short meditation sessions, can be seamlessly integrated into the school day. For instance, starting the morning with a five-minute breathing exercise can calm students' minds, setting a focused tone for learning. Mindfulness not only improves attention span but also aids in emotional regulation, helping students pause and think before reacting impulsively. Interactive Activities: Engaging and Educative Interactive activities that require students to follow instructions or work collaboratively can effectively boost their attention and self-control. Games like "Simon Says" or "Red Light, Green Light" require students to listen carefully and respond appropriately, honing their capacity to control impulses and focus on the task at hand. Additionally, activities that involve problem-solving or creative thinking—such as group projects or classroom debates—encourage students to concentrate and engage deeply with their peers and the material. Positive Reinforcement: Encouraging Growth Positive reinforcement plays a pivotal role in developing executive functioning skills. Praise and rewards for demonstrating self-control and attention can motivate students to replicate these behaviors. Teachers can implement systems such as token economies or recognition boards where students earn points or badges for exhibiting focused behavior. Celebrating these achievements fosters a classroom culture that values perseverance and self-regulation. Creating a Supportive Learning Environment Finally, fostering a supportive learning environment is essential. Teachers can create a space where students feel safe to make mistakes and are encouraged to learn from them. Implementing flexible seating arrangements or quiet zones can cater to different learning styles and help maintain focus. By cultivating a classroom atmosphere that respects individual needs and promotes positive interactions, teachers can significantly enhance students’ executive functioning abilities. By incorporating structured routines, mindfulness exercises, interactive activities, and positive reinforcement, teachers can play a pivotal role in developing students' attention and self-control. These skills are not only foundational for academic achievement but are vital for students’ overall personal growth and future success. As educators embrace these strategies, they prepare students to navigate the challenges of the modern world with confidence and competence. At GrapeSEED, we have embraced routine, interaction and creating an encouraging and supportive environment. As a matter of fact, these qualities are a large part of who we are and how our curriculum is structured. Want to learn more about us? Just click here!

As we continue on through our series about the different executive functioning skills, we’re learning that these skills are essential for academic success and everyday life. In today’s article, we’ll focus on how children can acquire the skills of taking initiative and remaining flexible and how teachers can help: Clear Expectations Teachers can help student start by establishing clear and concise instructions. Break tasks into smaller steps to make them manageable, reducing anxiety and promoting independence. This clarity encourages students to take initiative confidently. Visual Schedules Use visual schedules to map out the day's activities. These can include pictures or symbols that serve as cues for task initiation and help students anticipate transitions, making them more adaptable to changes. Adaptability Games Incorporate games that require quick thinking and adaptability, such as "Simon Says" or "Musical Chairs." These playful activities teach students to adjust their strategies and develop resilience in facing unexpected changes. Modeling Behavior Demonstrate the behaviors you wish to instill. By showing how to start tasks and adapt to disruptions, teachers offer a live example for students to emulate. Think aloud and verbalize your plans and adjustments to illustrate these processes. Positive Reinforcement Celebrate students' efforts in initiating tasks and adapting to change with positive reinforcement. Use praise, stickers, or privileges to acknowledge their progress, reinforcing these behaviors and building their confidence. Importance of These Skills Teaching task initiation and flexibility equips students with vital tools for success. These executive functioning skills prepare them for academic challenges and social interactions, laying a foundation for lifelong adaptability and independence. By integrating these strategies into classroom routines, teachers can effectively nurture students' executive functioning skills, helping them thrive in various settings. While the GrapeSEED curriculum is designed for English acquisition, it embodies so many of these powerful life skills. Click here for more!
Developing strong executive functioning skills, particularly planning and organization, is crucial for young students to thrive both academically and personally. As an elementary school staff member, you play a vital role in nurturing these abilities in your classroom. Here are some practical strategies that can be easily implemented to help your students build these essential skills. 1. Visual Schedules: A Roadmap for Success Visual schedules are an excellent tool for helping students understand and plan their day. By using charts or calendars with pictures, icons, or colors, you can guide students through their daily activities. This visual aid not only helps them anticipate what comes next but also fosters independence as they learn to follow their schedule. How to Implement: Create a daily schedule that includes all classroom activities. Use Velcro strips or magnets so that students can physically manipulate the schedule, adding or removing tasks as needed. Encourage students to check off completed tasks, giving them a sense of accomplishment. 2. Break Tasks into Manageable Steps Large tasks can be overwhelming for young learners. Breaking them down into smaller, more manageable steps makes them less daunting and easier to tackle, helping students initiate and complete their work confidently. How to Implement: When introducing a new project or assignment, outline each step on the board. Provide students with a checklist they can follow, ticking off each step as they complete it. Pair students with a buddy to discuss and divide tasks, promoting collaboration and peer learning. 3. Incorporate Games that Encourage Planni ng Games are a fun and effective way to develop planning skills. Activities that require strategy and foresight can help students learn to think ahead and plan their moves. How to Implement: Introduce board games like "Checkers" or "Connect Four," which require strategic thinking. Use puzzles that require students to plan their approach before starting. Organize team challenges where students must work together to achieve a goal, fostering both planning and collaboration. 4. Consistency is Key Consistency in your approach helps students understand the expectations and develop a habitual routine. When they know what to expect, they are more likely to engage in and initiate tasks independently. How to Implement: Establish a consistent classroom routine that students can rely on. Reinforce the importance of following the routine and provide gentle reminders as needed. Use consistent language and cues when discussing planning and task initiation. 5. Positive Reinforcement: Celebrate Small Wins Positive reinforcement is essential in motivating students and reinforcing good habits. Celebrating small achievements encourages students to take initiative and develop confidence in their abilities. How to Implement: Acknowledge and praise students when they successfully follow their schedule or complete a task. Use a reward system, such as stickers or a classroom reward jar, to recognize their efforts. Share success stories with the class, highlighting how planning and initiative led to positive outcomes. By incorporating these strategies into your teaching, you can create a supportive environment that empowers your students to develop crucial executive functioning skills. Remember, the goal is to provide them with the tools they need to plan effectively and to be organized. With consistency and encouragement, your students will be well on their way to becoming independent learners and thinkers. GrapeSEED’s carefully created curriculum is built on consistency, routine and building independence over time. Check us out by clicking here today!

In the dynamic world of childhood education, executive functioning skills play a pivotal role in shaping a child's learning and development. These skills act as the brain's control center, helping young learners manage their thoughts, actions, and emotions. Today, let’s explore the 10 key executive functioning skills essential for elementary school students and understand their impact on everyday learning and activities at a high level: 1.Planning Planning for young students involves setting simple goals, like completing a project or organizing a playdate. This skill helps them visualize steps needed to achieve their objectives. In a school setting, planning assists children in approaching assignments systematically and managing their time effectively. 2. Organization Organization means keeping school supplies, homework, and personal items in order. For elementary students, it translates to having a tidy desk or backpack. Organizational skills help students follow daily routines and reduce anxiety about misplaced items, leading to a more focused learning environment. 3. Task Initiation Task initiation is about starting homework or chores without delay. Young learners often struggle with procrastination, and this skill encourages them to begin tasks promptly. In the classroom, it helps students dive into activities or assignments as soon as they receive instructions. 4. Flexibility Flexibility allows children to adapt to changes, like classroom schedule shifts or unexpected challenges in projects. It encourages them to embrace new ideas and learn from mistakes. This skill is crucial for fostering creativity and resilience in learning. 5. Attention Attention helps children focus on their teacher's instructions or classwork while ignoring distractions. It is vital for absorbing new information and completing tasks efficiently. Improving attention can enhance a student's performance in subjects like reading and math. 6. Self-Control Self-control is the ability to manage impulses and emotions, such as waiting patiently for their turn or reacting calmly to a peer's comment. This skill supports positive interactions and helps maintain a conducive learning environment. 7. Metacognition Metacognition is thinking about one's own thought process. For children, it might involve reflecting on what strategies helped them learn a math concept or why a story was challenging to understand. This awareness boosts their ability to adjust learning tactics and improve academic success. 8. Working Memory Working memory enables students to hold and use information temporarily, such as remembering instructions or story details. It is crucial for following multi-step directions and participating in class discussions. Strengthening working memory supports academic achievement across all subjects. 9. Time Management Time management for elementary students involves learning how to allocate time for homework, play, and rest. It helps them balance schoolwork with leisure activities, reducing stress and improving their overall well-being. Mastering this skill can lead to more efficient and enjoyable school days. 10. Perseverance Perseverance is the determination to keep trying despite difficulties, like solving a tough math problem or learning a new sport. This skill teaches students resilience and encourages a growth mindset, essential for overcoming academic challenges and achieving goals. Nurturing executive functioning skills in elementary school students is crucial for their academic success and personal growth. By focusing on these areas, we can support children in becoming organized, adaptable, and resilient learners. Encouraging the development of these skills will not only enhance their educational journey but also set them on a path toward lifelong success. Be sure to check out this entire series, where we’ll take a deeper dive into each of the executive functioning skills. And be sure to check out what GrapeSEED can do for your English Language Learner and Emergent Multilingual Leaner students by clicking here .

“In diversity there is beauty and there is strength.” What does this powerful quote from Maya Angelou have to do with introducing your young students to special holidays celebrated by other children around the world? Plenty! Celebrating multicultural holidays in elementary schools is not just about recognizing different traditions; it's about creating an inclusive, respectful, and engaging learning environment. By incorporating these celebrations into the curriculum, teachers can enhance students' educational experiences and promote a more understanding and empathetic school community. Let's continue to embrace and honor the rich cultural tapestry that makes up our classrooms, one celebration at a time. Stories from the Classroom: "I've found that celebrating multicultural holidays has significantly increased my students' awareness and appreciation of different cultures. For example, during Diwali, we created rangoli patterns and learned about the significance of light in the festival. The students were fascinated and eager to learn more about Indian culture." - Mrs. Nguyen, 4th Grade Teacher "Last year, we celebrated Hanukkah alongside Christmas and Kwanzaa. It was amazing to see how much the students enjoyed learning about the similarities and differences between the holidays. This practice has helped build a classroom environment grounded in empathy and mutual respect." - Mr. Patel, 3rd Grade Teacher "Our school's multicultural holiday celebrations have brought parents and community members into the classroom. For Lunar New Year, several parents came in to share stories, food, and traditional games with the students. It was a beautiful way to strengthen the school-community bond." - Ms. Ramirez, 2nd Grade Teacher Tips for Getting Started: Begin by researching the cultural holidays that are significant to your student body. Consult with parents, community leaders, and colleagues to gain accurate and respectful insights into these traditions. Interactive activities such as crafts, music, food tasting, and storytelling can make the celebrations more engaging for students. These hands-on experiences can leave lasting impressions and make learning about different cultures fun and memorable. Developing a cultural calendar that includes important holidays from various cultures can help ensure that these celebrations are integrated throughout the school year. This approach allows students to anticipate and look forward to upcoming events. Encourage students to share their own cultural traditions and experiences. Creating an open and inclusive environment where every student feels valued and heard can enrich the multicultural celebration experience for everyone. GrapeSEED is proud to embrace teachers and students from all around the world. From Asia, to Europe, to the US, enriching the lives of children with our English acquisition curriculum so that they will flourish is our focus and goal. Ready to learn more about how you can get started with GrapeSEED in your classroom? Click Here

Ah, summertime! There’s no doubt, the carefree weeks of summer are an essential time for children to play, unwind and recharge before the beginning of the next school year. As we all know, the downside is that some of the learning and skills they’ve acquired from the prior year can slip away during this cherished time. Fortunately, there are many ways to prevent students from having a “summer slide” while still being able to just be kids.

There’s just no doubt about it, teachers of multilingual learner children want nothing but the very best for their students. And while one curriculum always seems to be working to “one-up” the other, the natural language acquisition approach always seems to come out on top! Why? Because this preferred method encourages newcomer students to learn English like they learned their heritage language—through immersion, play, and discovery.
As an ELL educator, one of the greatest struggles I’ve had over the years is finding a comprehensive program that can support effective English language acquisition for my emergent bilingual Pre-K, kindergarten, and first-grade students who are acquiring English. Without the proper resources, the journey to better English proficiency was tedious, challenging, and overwhelming. As a teacher who has experienced this hardship firsthand, I can assure you that the GrapeSEED English program is making a massive difference in the lives of my students. The curriculum, which includes repetitive opportunities for movement, songs, chants, poems, and stories, is enriching and I have seen significant growth in my students since beginning to use the program! I only wish it had been around when I was a small child, new to the United States!

It’s no secret that in today's society, our focus on mental health has been brought to the forefront. Children, too, have mental health needs that we, as educators, are in a unique position to positively impact. We have the opportunity to play an essential role in fostering emotional wellness for each child in our charge. It goes without saying that from time to time, families should be guided to mental health professionals to intervene. But by implementing the following six tips, we can help create a supportive environment that fosters the mental health of our students, helping them become confident, happy, and successful in the classroom and beyond.

Ah, December. The festive season that brings about joy, cheer, and... anxiety? As teachers, we all know that December can be a challenging month with overloaded schedules and high-energy students excited for the holidays. Read on as we discuss five practical strategies to help you to survive the month of December, to keep your classroom as tranquil as possible, and to have a very happy holiday break.

With Thanksgiving fast approaching, enjoying succulent turkey leg and rich, yummy pumpkin pie are the least of our thoughts. Instead, we’re taking a moment to reflect on what we’re grateful for. Our administrator and teacher friends have shared what they’re thankful for, and the responses they gave were inspiring. We’re excited to share their thoughts with you!
Involve your students' parents and families by inviting them into the classroom to share traditions of their home countries.

Field trips are integral to education, and they can be especially meaningful for English language learners! Visiting a new place and learning in an immersive environment can be a great way to learn and practice English. Check out a few meaningful tips to make field trips meaningful for English language learner students:
Have you ever been to a preschool classroom and heard nothing but the sound of crickets? If so, you probably left feeling like something was missing. That something is chatter—the sweet sound of little voices discussing their ideas and exploring the world around them. Chatter can be just as important for learning as books, pencils, and puzzles. Let’s take a look at why preschoolers need opportunities to engage in oral language.

I love this quote from writer, speaker, and coach Todd Stocker: “I wanted to figure out why I was so busy, but I couldn’t find the time to do it.” It’s true that in educators’ worlds today, everyone is busier than ever! Even when we aren’t in the classroom, at a staff meeting, or out in the community, we’re still always ‘on.’ That’s why we were thrilled when twenty-two-year veteran ELL teacher, Brooke Mindnich, from Eatontown, NJ made time to share about her experience with the GrapeSEED curriculum.

If you’re like most folks, when you hear the word ‘newcomer’ you likely envision an adult person bravely setting out to build a new life in a new place. Most of us realize the that inevitable challenges will come with acclimating to a foreign country, to surprising new social norms, to a foreign language and everything that beginning life in a new place might entail.

What’s the first step in language acquisition? Learning to hear and form new sounds that will eventually lead to producing language! The technical term here is ‘phonemic awareness’, but what it boils down to is being able to recognize and manipulate sounds within the context of words. Be it a toddler beginning to put sounds together as they learn to talk, or an older child or adult learning a second or even third language, the ability to hear distinct sounds within words and the ability to reproduce those sounds is all part of the process.
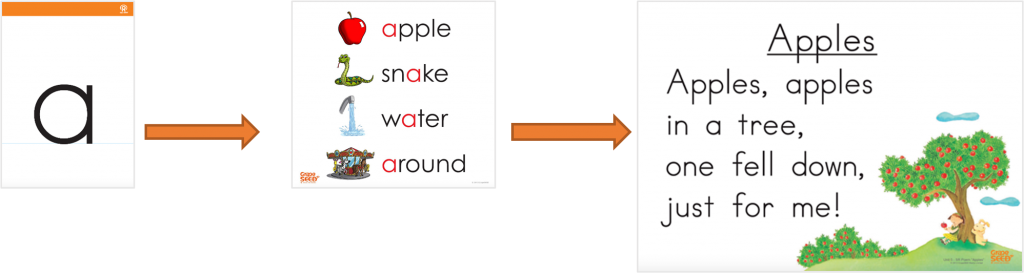
If you’re in education, you know that there has been endless debate around the subject of phonics: whether to teach it, how to teach it, and how often to teach it. Fortunately, reading scientists seem to have finally put this debate to rest, and the research findings are clear! Students that receive phonics instruction in the classroom and during a consistent, designated intervention time have a serious advantage over those that do not receive phonics instruction (Chapman, Greaney, & Turner, 2015; National Reading Panel, 2000; Snow, Burns, & Griffin, 1998). With the GrapeSEED curriculum, our approach to phonics instruction is powerful, unique, gets results, and aligns with The Science of Reading’s framework.
Are you thinking to yourself, ‘what role does an oral language curriculum designed for young students to acquire English have to do with structural analysis?’. The answer is ‘everything’! Let’s jump right in and start with defining structural analysis. To put it simply, structural analysis is the ability to break unfamiliar words down into smaller parts. In other words, once students achieve sound-symbol correspondence and can apply this knowledge to decode one syllable words, they can then begin to focus on those meaningful word parts that will help them to develop skills to read and understand more complex, multisyllabic words. That, of course, is why structural analysis is at the heart of Science of Reading. Structural analysis relies on using multiple elements to develop a student's capacity to comprehend unfamiliar words. Your students may have the ability to decode words, but without a firm foundation in oral language and of word meaning, their comprehension in English will be negatively impacted.

Celebrity Tim Gunn said it this way, “Few activities are as delightful as learning a new language.” And it’s true! Being able to speak even the most basic words…colors, days of the week, numbers… in a language other than our heritage language, whatever that may be, brings a smile and sense of pride to us all.











